Scientists at the Veterinary Service Department and the CSIR – Animal Research Institute have confirmed IBV in Ghana’s poultry industry
The IBV impacts the respiratory, reproductive, and renal systems of chickens, leading to severe economic repercussions. Originating in the USA during the 1930s, IBV has since spread globally, including sub-Saharan Africa, with Ghana being notably affected. Despite the significant presence of IBV, vaccination against the virus in Ghana is not practiced, complicating efforts to control its spread.
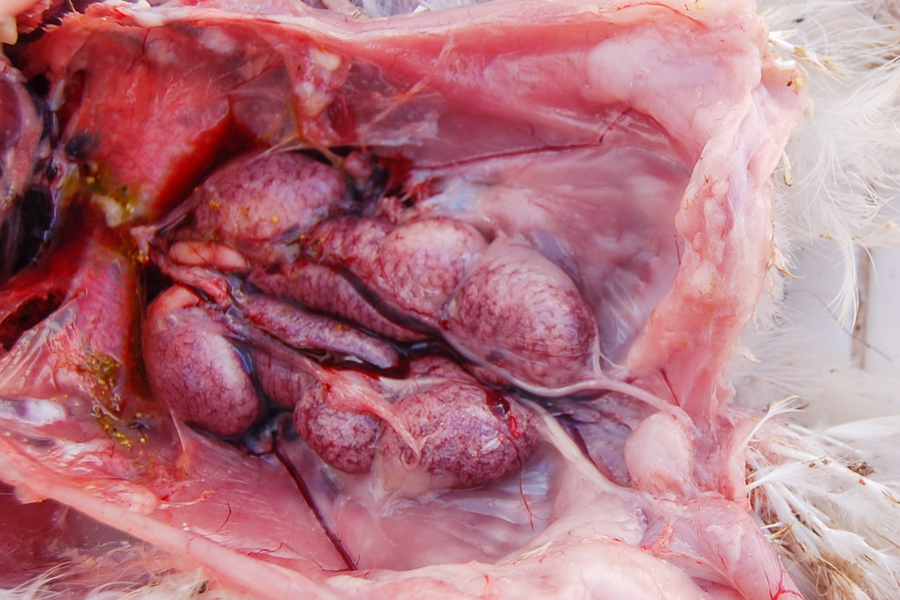
Samples collected by scientists at the Veterinary Service Department and the CSIR – Animal Research Institute from farms across nine regions revealed the presence of IBV, a coronavirus causing significant economic losses. The virus leads to reduced poultry output, lower egg production, and a 5% mortality rate.
In a Channel One News interview during a stakeholders’ workshop in Koforidua, Senior Research Scientists at the Animal Research Institute, Dr Matilda Ayim Akonnor and Dr Theophilus Odoom discussed their findings on IBV’s prevalence, serotypes, and pathotypes in Ghana. They highlighted that IB (Infectious Bronchitis) is a major factor behind the closure of many poultry farms in the country.
Dr Akonnor stated, “Indeed, we have confirmed that the virus is present in all nine regions we visited. We have taken samples, analysed some, and confirmed the virus’s presence. We have also identified the serotype that is circulating around the country from outbreak investigations, and we hope to use this information to develop a vaccination schedule for the country’s poultry farmers.”